Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) allows remote administration of Windows systems over a network connection. It enables users to access GUI desktops, applications, files, and network resources on a remote host machine as if they were sitting in front of it. RDP uses the client-server model and transmits data over a TCP-based protocol.
By default, RDP listens on TCP port 3389 for incoming connections. While convenient, this well-known port number makes RDP vulnerable to attacks. Attackers and malware routinely scan network address ranges looking for open RDP ports to compromise. Therefore, it is highly recommended to change the default port if RDP is required.
Reasons to Change the Default RDP Port
Here are some key reasons to change the default RDP port:
- The port 3389 is one of the most frequently scanned ports by attackers looking for vulnerable systems. Changing it reduces the attack surface.
- Obscurity provides an extra layer of security. Attackers will have to work harder to find which port is actually used for RDP. A non-standard port will evade many automated scripts.
- It breaks reconnaissance efforts from attackers and malware relying specifically on port 3389 being open. They will miss this RDP service in scans.
- Changing ports allows running multiple RDP services on one IP address by assigning them different ports.
- In case of compromise, it adds delays for attackers as they have to first find where RDP is listening before proceeding with lateral movement efforts.
- If RDP is only used as a backup access method, a non-standard port prevents most external reconnaissance.
How to Change the Default RDP Port
If you want a fast and hassle-free way to change your RDP port, we’ve got you covered! Instead of manually editing the registry, you can use our automated script to change the RDP port, update firewall rules, and restart the necessary services in one go.
Download the Change RDP Port Script
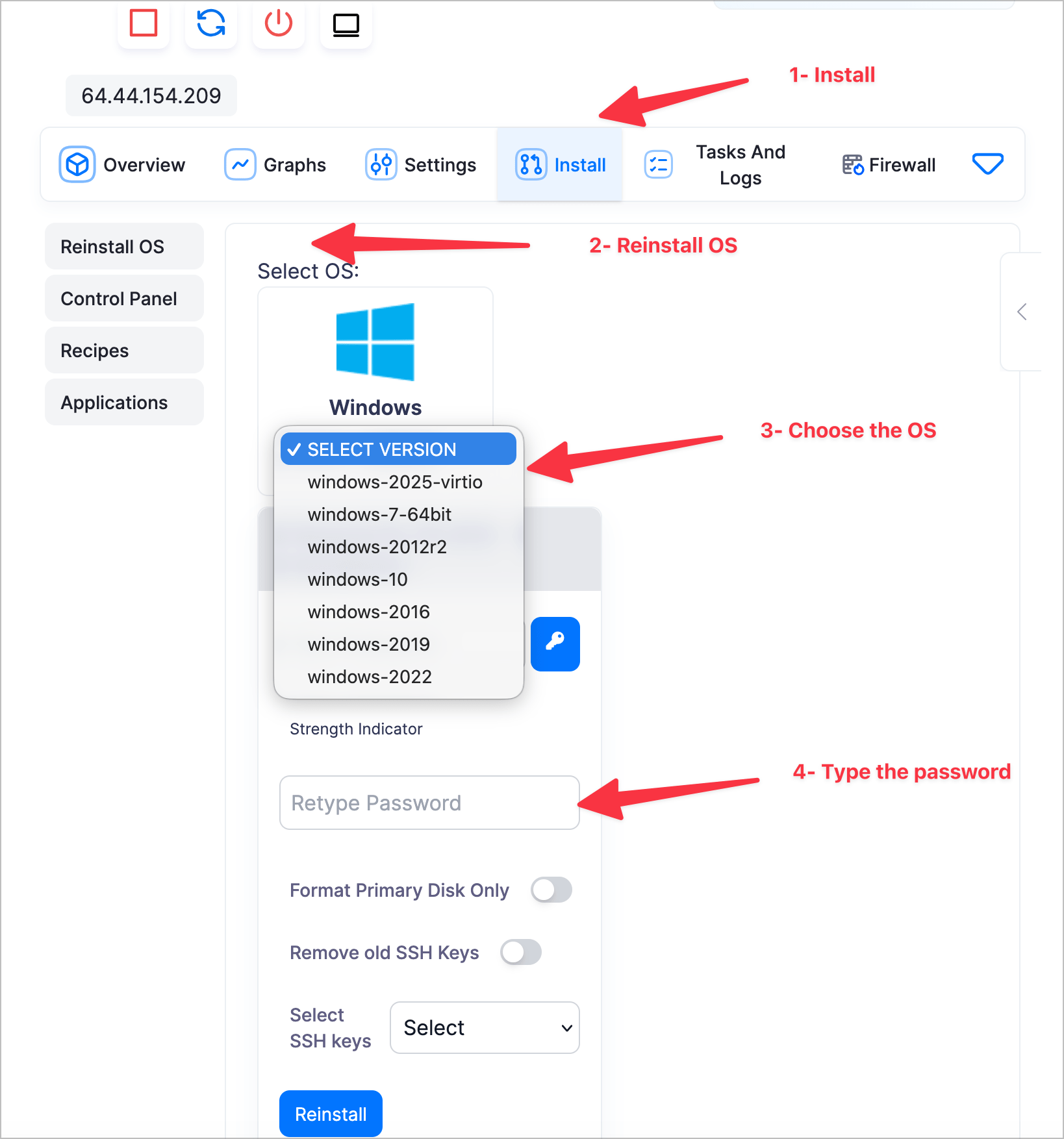
If you prefer to do it manually, follow the step-by-step guide below.
The RDP port can be changed by modifying a registry setting on Windows machines:
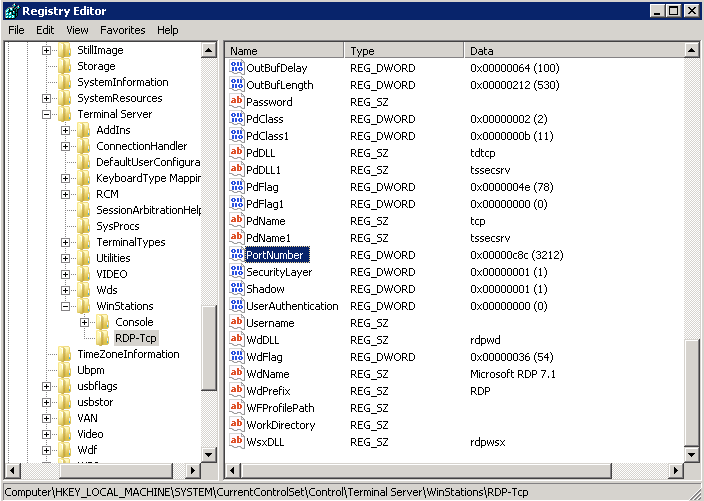
- Open the Run dialog by pressing Windows + R and type “regedit” to launch the Registry Editor with admin rights.
- Navigate to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- In the right-pane, locate the “PortNumber” DWORD value and double-click to modify it.
- Change the value data field to a custom port like 33389 and click OK. Avoid using common ports such as 22, 25 etc.
- Update firewall rules on the local and remote ends to allow the new port inbound.
- Reboot the system for changes to take effect.
- Notify legitimate users of the new RDP port to use when connecting remotely.
Extra Security Best Practices
In addition to changing the default port, implement these extra security measures:
- Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA) which requires authentication before an RDP session is created.
- Use account lockouts after a set number of failed login attempts to prevent brute force.
- Mandate the use of strong randomized passwords that are regularly changed.
- Use IP address allow-listing to only permit RDP from specific trusted public IP addresses.
- Set an account expiration date in Active Directory after which credentials must be refreshed.
- Restrict RDP access to select admin groups and accounts instead of enabling it broadly.
- Use a remote access VPN for additional encryption of RDP traffic when travelling or on untrusted networks.
Conclusion
The default RDP port 3389 provides an easy attack vector for malicious actors to target. While changing the port does not resolve all RDP security issues, it can effectively eliminate many automated small-scale attacks and slow down targeted efforts. Combined with additional safeguards, it is a simple hardening measure that adds tangible benefits by removing low-hanging fruit.